Motivation
Combinations of multiple software packages developed by different groups are essential for large-scale computational science, where the capabilities needed for modeling, simulation, and analysis are broader than any single team has resources to address. The often tedious trial-and-error process of obtaining, configuring, and installing any single tool may arguably be manageable. However, from the perspective of an end-user application scientist, handling each tool’s installation idiosyncrasies can easily become overwhelming when dealing with several packages in combination. Worse, such problems are compounded by the need for consistency among packages to be used within the same application in terms of compiler, compiler versions and options, and common third-party packages such as BLAS and HDF5.
Spack
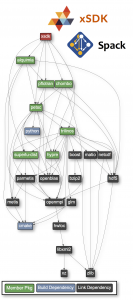
A goal of the xSDK is to simplify the process of working with various xSDK packages in combination. Spack is a package manager for high-performance computing. We thus provide an xSDK Spack metapackage that includes, by default, the four initial xSDK numerical libraries (hypre, PETSc,SuperLU_dist, and Trilinos) as well as some commonly needed external packages.
Spack allows the xSDK packages to be deployed with a single command. The user can optionally choose compilers, MPI implementation, and build options. We are working toward support of combinatorial test dashboards for all xSDK packages.
xSDK 0.2.0 release components
Release date: February 28, 2017
The xSDK spack metapackage (version 0.2.0) includes tested development versions of the following xSDK packages:
- hypre
- PETSc
- SuperLU, SuperLU_DIST
- Trilinos
- Alquimia
- PFLOTRAN
Note: Chombo is not currently included in the 0.2.0 alpha version of the xSDK, but has satisfied all xSDK required policies.
How to install xSDK 0.2.0
1. Obtain and install Spack.
See details about obtaining and using Spack.
You can clone Spack from the github repository using this command:
git clone https://github.com/llnl/spack.git
After cloning, set up the environment variables.
# For bash users $ export SPACK_ROOT=/path/to/spack $ . $SPACK_ROOT/share/spack/setup-env.sh # For tcsh or csh users (note you must set SPACK_ROOT) $ setenv SPACK_ROOT /path/to/spack $ source $SPACK_ROOT/share/spack/setup-env.csh
2. Make sure proxy settings are set appropriately.
For those who are interested in using xSDK on desktop/laptop machines, make sure that proxy settings are set appropriately. Otherwise, Spack will fail to “fetch” the packages of your interest.
For bash:
export http_proxy=<your proxy URL> export https_proxy=<your proxy URL>
For csh/tcsh:
setenv http_proxy <your proxy URL> setenv https_proxy <your proxy URL>
3. Edit packages.yaml file to specify the system-build software packages for xSDK installation.
Although Spack is updated regularly, we recommend using your own CMAKE and python installation, especially for the Mac OS X environment. In order to use your CMAKE and python, edit the $SPACK_ROOT/etc/spack/defaults/packages.yaml file. The following is an example for Mac OS X (the bold characters are added to the original yaml file).
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
# This file controls default concretization preferences for Spack.
#
# Settings here are versioned with Spack and are intended to provide
# sensible defaults out of the box. Spack maintainers should edit this
# file to keep it current.
#
# Users can override these settings by editing the following files.
#
# Per-spack-instance settings (overrides defaults):
# $SPACK_ROOT/etc/spack/packages.yaml
#
# Per-user settings (overrides default and site settings):
# ~/.spack/packages.yaml
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------
packages:
all:
compiler: [gcc, intel, pgi, clang, xl, nag]
providers:
mpi: [openmpi, mpich]
blas: [openblas]
lapack: [openblas]
awk: [gawk]
pil: [py-pillow]
cmake:
paths:
cmake@3.7.2: /Applications/CMake.app/Contents
buildable: False
python:
paths:
python@2.7.10: /usr
buildable: False
After the edit, xSDK packages and external dependencies (as shown in the above figure) can be installed with a single command:
spack install xsdk
Other useful options for the Mac packages.yaml file include:
# Apple provided packages
m4:
paths:
m4@1.4.6: /usr/bin
buildable: False
zlib:
paths:
zlib@1.2.8: /usr/
buildable: False
# homebrew provided packages
# install with: brew install packagename
autoconf:
paths:
autoconf@2.69: /usr/local/bin
buildable: False
libtool: # note it installs it with the name glibtool to avoid conflict with Apple's libtool
paths:
libtool@2.4.6: /usr/local/bin
buildable: False
mpich:
paths:
mpich@3.2: /usr/local
buildable: False
# openmpi:
# paths:
# openmpi@2.0.1: /usr/local
# buildable: False
# python: # you should also be able to use the Apple provided python; see below
# paths:
# python@2.7.12: /usr/local
# buildable: False
boost:
paths:
boost@1.62.0: /usr/local
buildable: False
# NVIDIA provided CUDA tools from Nvidia.com
cuda:
paths:
cuda@8.0: /Developer/NVIDIA/CUDA-8.0
buildable: False
4. Install environment modules.
Environment modules are not typically pre-installed in a generic Linux client or Mac OS X environment. Skip this process if your environment already has modules installed. Otherwise, Spack manages the installation for you.
spack install environment-modules
After the installation, the module is enabled by the following command line.
For bash:
source `spack location -i environment-modules`/Modules/init/bash
For tcsh:
source `spack location -i environment-modules`/Modules/init/tcsh
5. Load xSDK module and its sub-modules.
Now you can load xSDK environment. Try Spack’s load command with the -r (resolve all dependencies) option:
spack load -r xsdk
Then, module list generates the following output, for example:
Currently Loaded Modulefiles: 1) xsdk-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-cf2thqr 2) xz-5.2.3-clang-8.0.0-apple-g5ufgu4 3) zlib-1.2.11-clang-8.0.0-apple-t6ww3wg 4) libxml2-2.9.4-clang-8.0.0-apple-35qx5im 5) hwloc-1.11.6-clang-8.0.0-apple-3glzbi4 6) openmpi-2.1.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-tvdag7h 7) hdf5-1.10.0-patch1-clang-8.0.0-apple-dxxd6gu 8) openblas-0.2.19-clang-8.0.0-apple-zu27hwi 9) hypre-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-ijslryx 10) metis-5.1.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-cjfdadm 11) parmetis-4.0.3-clang-8.0.0-apple-lxfa6fo 12) superlu-dist-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-id52gbr 13) bzip2-1.0.6-clang-8.0.0-apple-kekvvku 14) boost-1.63.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-bdbp4oj 15) glm-0.9.7.1-clang-8.0.0-apple-wwmtkwa 16) matio-1.5.9-clang-8.0.0-apple-lqnaazr 17) netcdf-4.4.1.1-clang-8.0.0-apple-7ctr2ac 18) trilinos-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-5vbf6fd 19) petsc-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-yfnvas2 20) pflotran-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-w2lrquh 21) alquimia-xsdk-0.2.0-clang-8.0.0-apple-7sxf5fo
xSDK 0.2.0 platform testing
xSDK 0.2.0 has been updated/fixed on a regular basis in collaboration with ALCF, NERSC, and OLCF to fully test xSDK packages on key machines at these DOE computing facilities. The Spack xSDK installer has been tested on the following machines:
- Linux with GNU (5.4.0 and 6.3.0) compilers, both static and shared libraries.
- Mac OS X (10.11 and 10.12) with Clang-8.0.0 compilers both static and shared libraries.
- DOE high-end computing systems at ALCF, OLCF, NERSC:
- ALCF: Mira: IBM BlueGene with Gnu compilers
- Cannot build with IBM compilers or gcc-4.4.7 since they do not support C++11 needed by Trilinos.
- The hdf5 supplied for gcc-4.8.4 does not have the fortran .mod files needed for some packages
- Set up the gcc-4.8.4 toolchain
-
soft add +bgqtoolchain-gcc484
- compilers.yaml
-
compilers: - compiler: modules: [] operating_system: cnk paths: cc: /soft/compilers/gcc/4.8.4/bin/powerpc64-bgq-linux-gcc cxx: soft/compilers/gcc/4.8.4/bin/powerpc64-bgq-linux-g++ f77: soft/compilers/gcc/4.8.4/bin/powerpc64-bgq-linux-gfortran fc: /soft/compilers/gcc/4.8.4/bin/powerpc64-bgq-linux-gfortran spec: gcc@4.8.4 - packages.yaml
-
packages: mpich: paths: mpich@3%gcc@4.8.4:bgsys/drivers/ppcfloor/comm/gcc buildable: False netcdf: paths: netcdf@4.3.3%gcc@4.8.4: /soft/libraries/netcdf/4.3.3-f4.4.1/cnk-gcc/V1R2M2-20150514 buildable: False hdf5: paths: hdf5@1.8.12%gcc@4.8.4: /home/sarich/software/hdf5/1.8.12/gnu484 buildable: False cmake: paths: cmake@3: /soft/buildtools/cmake/current buildable: False zlib: paths: zlib@1.2.11: /soft/libraries/alcf/current/gcc/ZLIB buildable: False python: paths: python@2.6: /usr buildable: False m4: paths: m4@1.4.17%gcc@4.8.4+sigsegv: /usr buildable: False all: compiler: [gcc@4.8.4] variants: ~shared providers: mpi: [mpich@3] blas: [netlib-lapack] lapack: [netlib-lapack] - NERSC: Edison: Cray with Gnu compilers
- ALCF: Mira: IBM BlueGene with Gnu compilers
-
-
-
- Exact options used on Edison:
module load mercurial spack install xsdk%gcc@6.1.0
- Exact options used on Edison:
- packages.yaml
packages: mpich: modules: mpich@7.4.1%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : cray-mpich/7.4.1 buildable: False hdf5: modules: hdf5@1.8.12%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : cray-hdf5-parallel/1.8.12 buildable: False netcdf: modules: netcdf@4.3.1%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : cray-netcdf-hdf5parallel/4.3.1 buildable: False zlib: modules: zlib@1.2.7%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : zlib/1.2.7 buildable: False boost: modules: boost@1.54%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : boost/1.54 buildable: False cmake: modules: cmake@2.8.12.2%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : cmake/2.8.12.2 buildable: False python: paths: python@2.7.9%gcc@6.1.0 arch=cray-CNL-ivybridge : /usr/common/software/python/2.7.9 buildable: False all: providers: mpi: [mpich]
-
-
-
- OLCF: Titan: Cray with gnu compilers.
- Load the appropriate modules:
-
module load modules module swap PrgEnv-pgi PrgEnv-gnu module swap gcc gcc/5.3.0 module load cmake3 module load cray-hdf5-parallel/1.8.14 module load mercurial
- Work around openblas failure by removing check_build:
- In var/spack/repos/builtin/packages/openblas/package.py change:
make('tests', *self.make_defs)
to
#make('tests', *self.make_defs)
spec = self.spec - Comment out:
output = compile_c_and_execute(source_file, include_flags, link_flags)
compare_output_file(output, blessed_file)
- In var/spack/repos/builtin/packages/openblas/package.py change:
- Create ~/.spack/cray folder
- Create packages.yaml
packages: mpich: modules: mpich@7.4.0%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray: cray-mpich/7.4.0 mpich@7.4.0%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos: cray-mpich/7.4.0 buildable: False cmake: paths: cmake@system: /sw/xk6/cmake3/3.2.3/sles11.3_gnu4.3.4/bin/cmake cmake@7.4.0%gcc@5.3.0: /sw/xk6/cmake3/3.2.3/sles11.3_gnu4.3.4/bin/cmake version: [system] buildable: False hdf5: paths: hdf5@1.8.14%gcc@5.3.0: /opt/cray/hdf5-parallel/1.8.14/GNU/5.1 version: [1.8.14] buildable: False boost: modules: boost@1.60.0%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos: boost/1.60.0 buildable: False perl: modules: perl@5.20.2%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos: perl/5.20.2 buildable: False python: modules: python@2.7.9%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos: python/2.7.9 python@3.5.1%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos: python/3.5.1 buildable: False mercurial: modules: mercurial@2.6.3%gcc@5.3.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos: mercurial/2.6.3 buildable: False all: providers: mpi: [mpich] - Create compilers.yaml (optional, spack will generate, see link)
- Install:
./spack -vd install xsdk@xsdk-0.2.0 arch=cray-CNL-interlagos
- OLCF: Titan: Cray with gnu compilers.
Users who prefer to work with just one xSDK package rather than several can use Spack to install only that particular package. Alternatively, they can bypass Spack and instead obtain the package directly from its website and install according to instructions there.
Open source packages installed with xSDK packages
Users can view a tree of dependencies for any Spack package, including xSDK, by running ‘spack spec’. This is the dependency tree for the xSDK metapackage:
xsdk ^hypre@develop~internal-superlu ^blas ^lapack ^mpi ^petsc@develop~boost+hdf5+hypre+metis+mpi~mumps+superlu-dist+trilinos ^hdf5@1.8.12:+fortran+mpi ^zlib@1.2.5: ^parmetis ^cmake@2.8: ^metis@5: ^python@2.6:2.7 ^bzip2 ^ncurses ^openssl ^perl@5.14.0: ^readline ^sqlite ^sowing ^trilinos@develop+boost+hdf5+hypre+metis~mumps~suite-sparse+superlu-dist+xsdkflags ^boost ^glm ^matio ^netcdf+mpi ^m4 ^superlu-dist@develop ^pflotran@develop ^xsdktrilinos@develop
The following open source HPC packages are installed by default with the xSDK. Note that you may override these and use a preinstalled version if you wish.
If Alquimia (an xSDK biogeochemistry package) is installed with the option “+alquimia”, then PFLOTRAN also needs to be installed, which is used by Alquimia as one of its chemistry engines.